Podocarpaceae
Podocarpus salignus
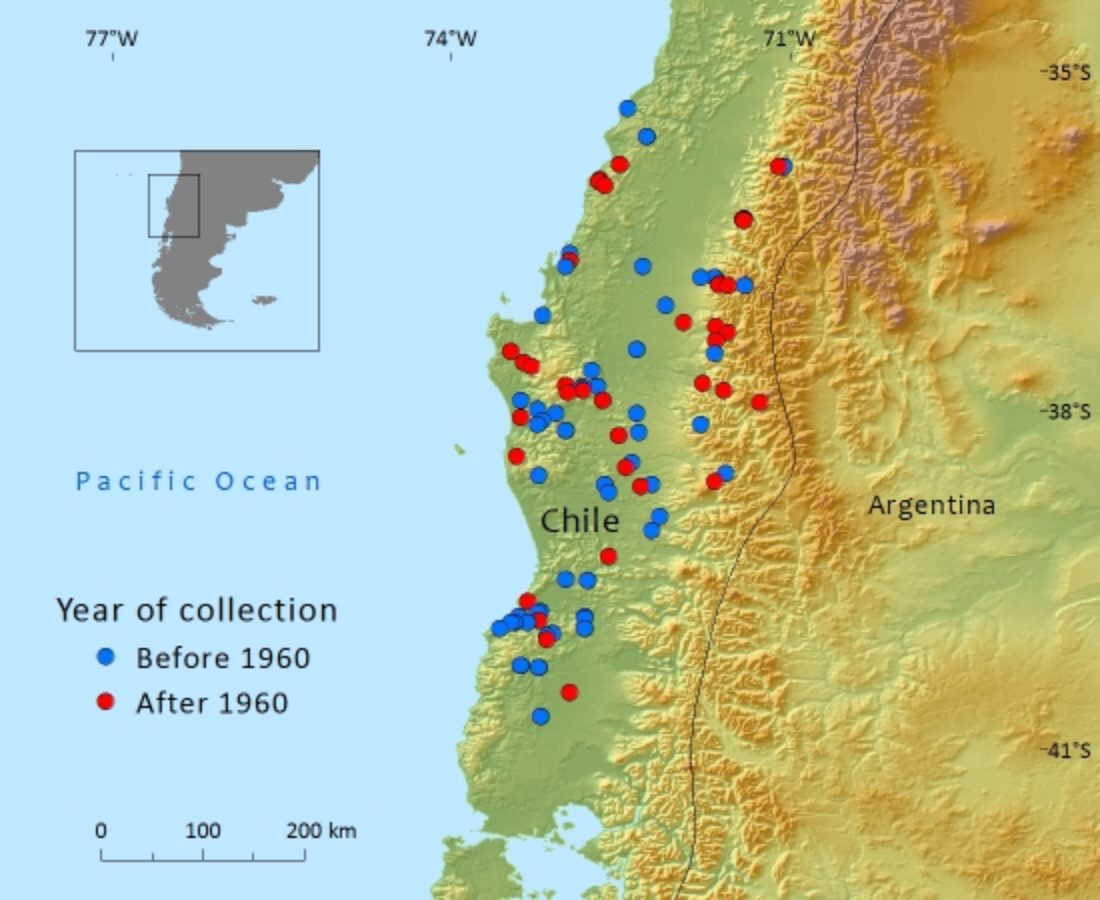
Podocarpus salignus is endemic to central and southern Chile where there has been reduction of its habitat due to landuse change.
Description
Habit
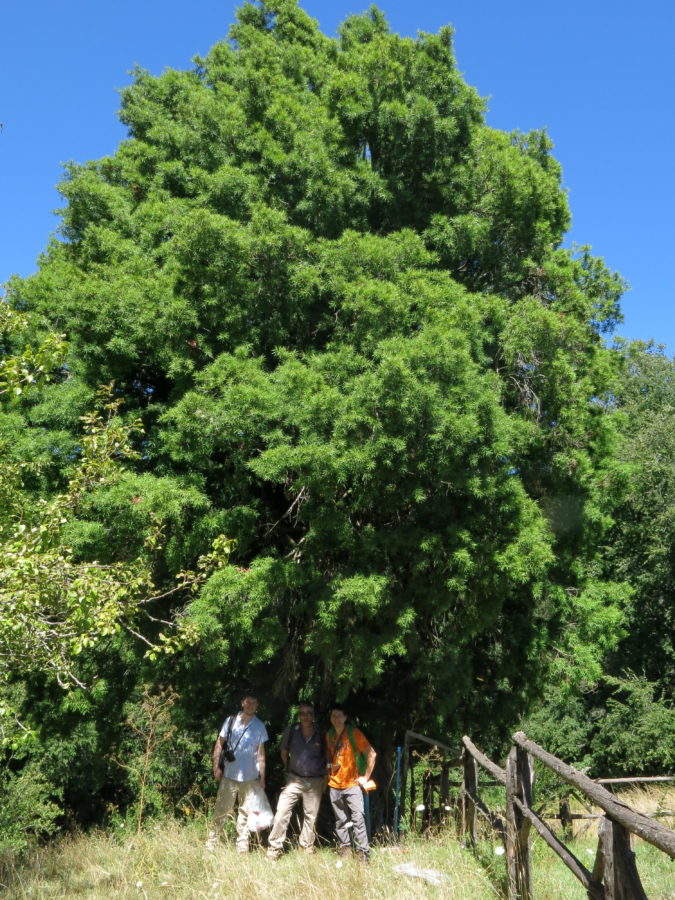
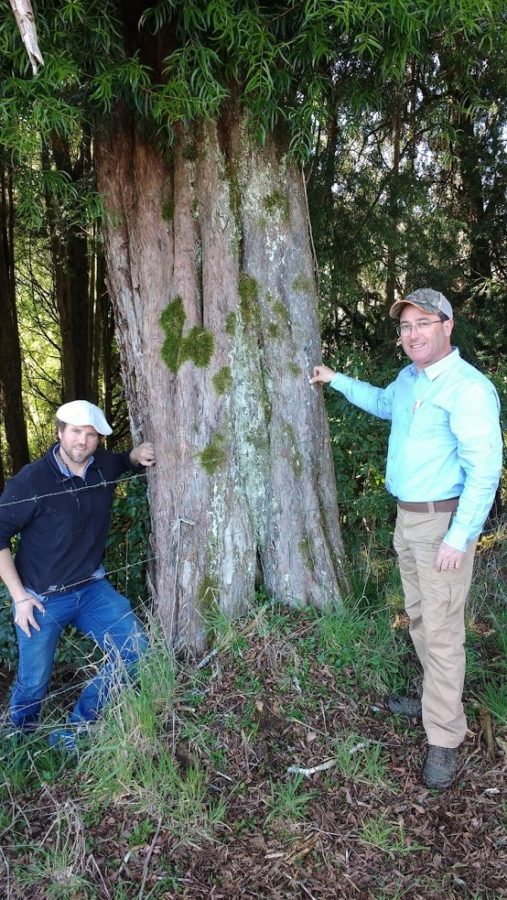
Dioecous tree up to 20m tall. Canopy pyramidal and more or less rounded. Trunk up to 1m in diameter. Bark has thin plates in older specimens, greyish.
Foliage
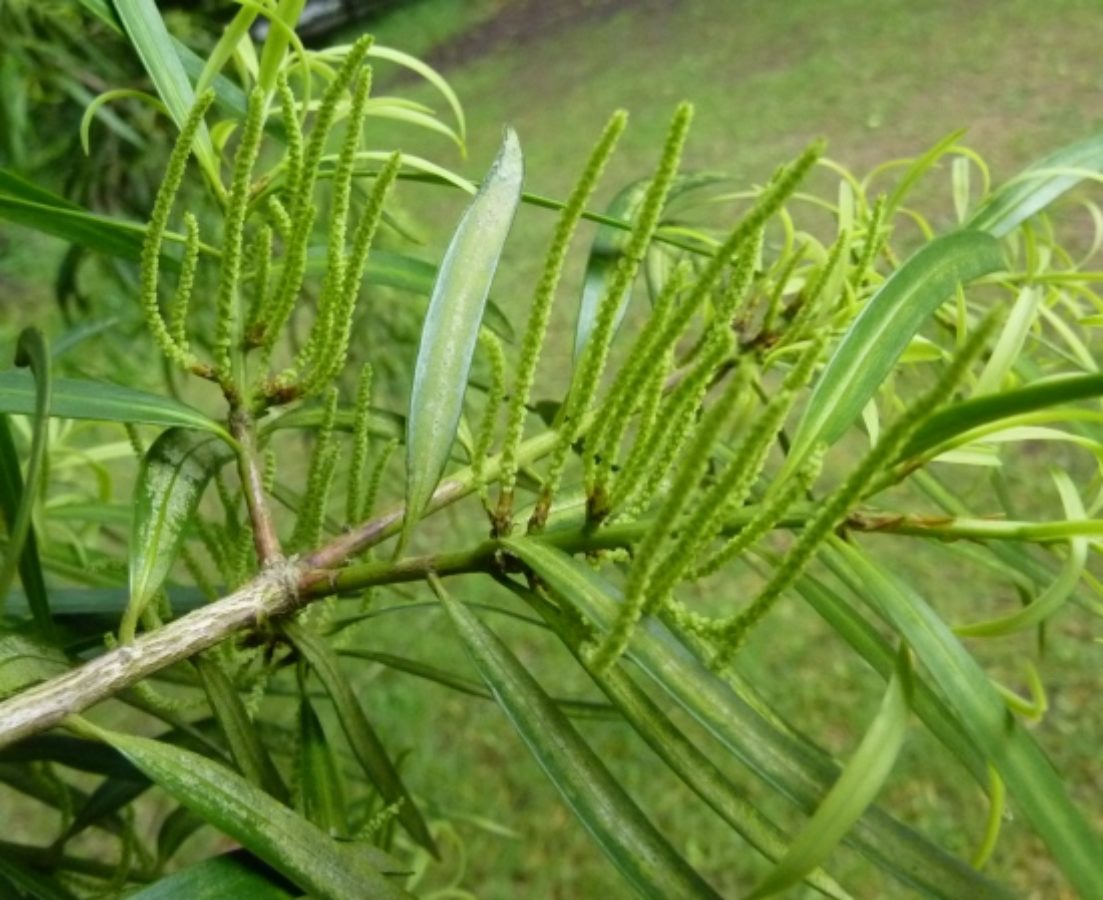
Leaves 5–10 x 0.6–0.7cm, linear-lanceolate, slightly falcate, simple, alternate, pendulous, pointed at the apex.
Cones
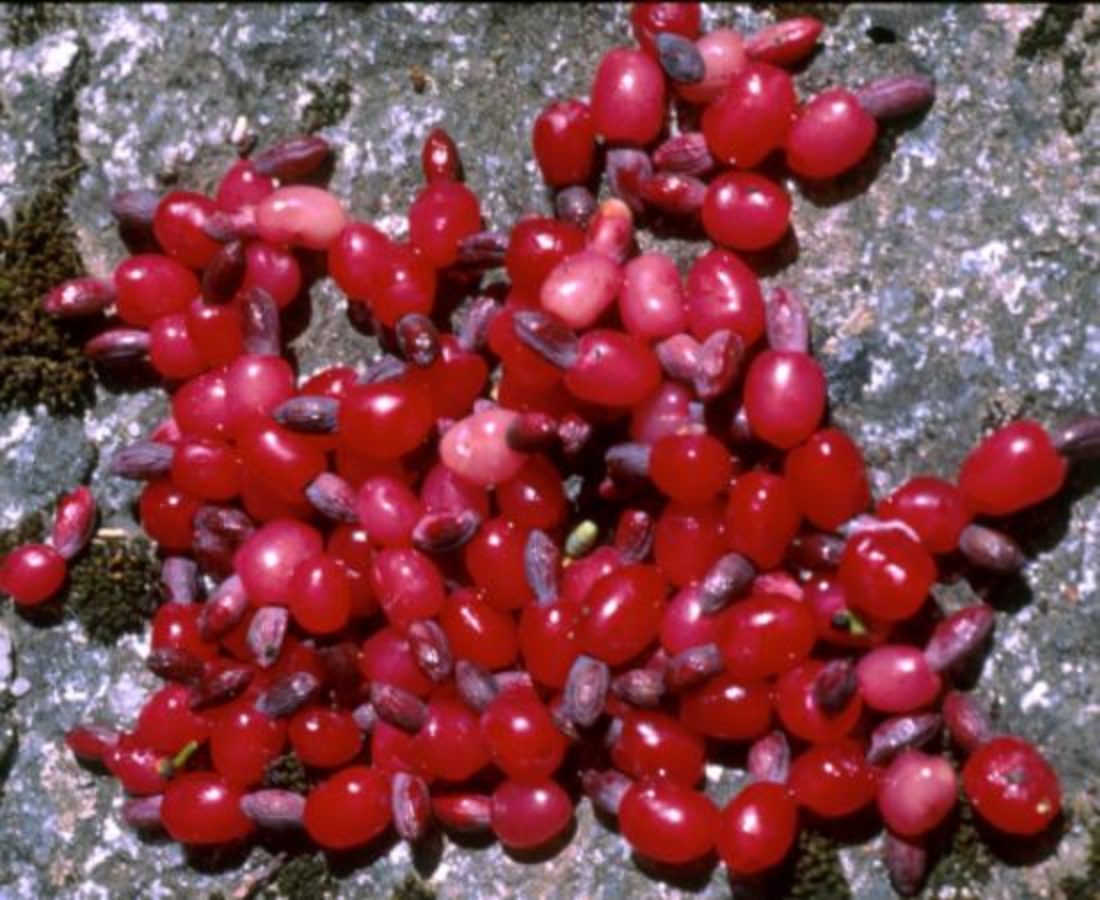
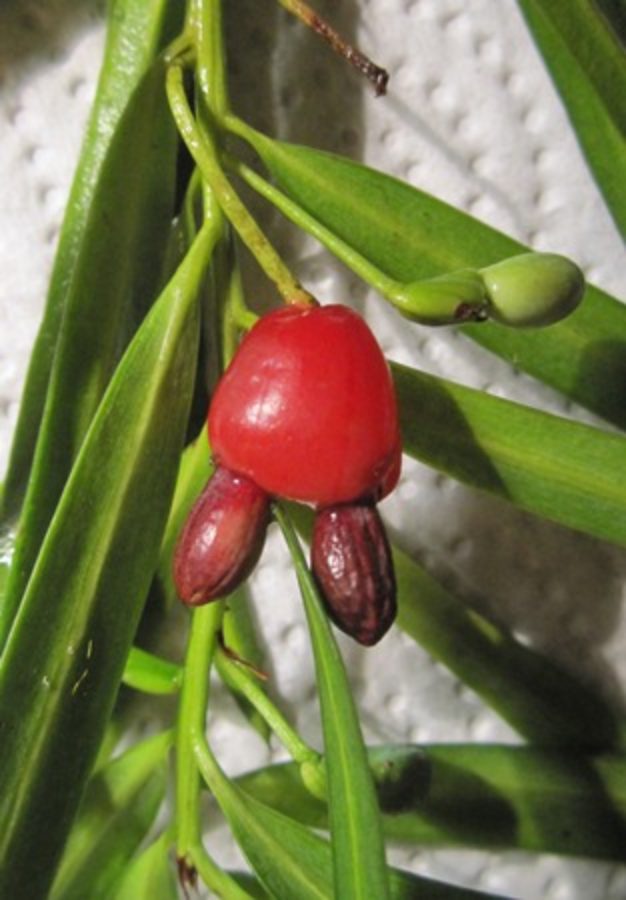
Male pollen-cones 2.2–5cm, solitary or grouped, sessile. Female seed-cones, solitary, axillary, peduncle 1–1.5cm long; flowering between december and january. Seeds 1–2, 7–8 x 4mm, red and subtended by a fleshy, violet-red aril; fruits maturing from January to May.
Human Uses
This species has not been widely utilized for its timber (Donoso, 2006). The foliage is commonly used in the cut flower industry in Chile and the species is often grown in temperate countries as an ornamental tree. In Britain and Ireland there are some notable specimen trees from the original introduction from Chile during the mid 19th century and in some of these sites there is abundant regeneration.
References and further reading
- Allnutt, T. R., Courtis, J. R., Gardner, M. F. & Newton, A .C. (2001). Genetic Variation in Wild Chilean and Cultivated British Populations of Podocarpus salignus D. Don (PODOCARPACEAE). Edinburgh Journal of Botany 58(3): 459-473.
- CONAF, CONAMA, BIRF, Universidad Austral de Chile, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile and Universidad Católica de Temuco. (1999). Catastro y evaluatión de los Recursos Vegetacionales Nativos de Chile. Informe Nacional con Variables Ambientales. Santiago, Chile.
- Concha, M.C. (1995). Rol de los claros en la regeneración natural de Podocarpus saligna, en un bosque valdiviano (San Martín). Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad Austral de Chile.
- Donoso, Z.C. (ed.). (2006). Las especies arbóreas de los bosques templados de Chile y Argentina. Autoecología. pp. 678. Marisia Cuneo Ediciones, Valdivia, Chile.
- Gardner, M. 2013. Podocarpus salignus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2015.2. <www.iucnredlist.org>.
- Gastman, E. (1988). Propagación vegetativa de coniferas chilenas con aptitudes ornamentales. Facultad de Ciencias Agarias, Universidad Austral de Chile.
- Hechenleitner, P., Gardner, M. F., Thomas, P., Echeverría, C., Escobar, B., Brownless, P. & Martínez, C. (2005). Plantas amenazadas del Centro-Sur de Chile. Distribución, Conservación y Propagación. Universidad Austral de Chile y Real Jardín Botánico de Edimburgo, Santiago.
- Rodríguez, R. R., Matthei, O. & Quezada, M. (1983). Flora Arbórea de Chile. Universidad de Concepción, Concepción (Chile).
- Stoll, A. & Hahn, S. (2007). Nuevos registros extienden el limite Septentrional de once especies Valdivianas al norte del Rio Maule, Chile. [New records extend the distribution of eleven Valdivian species to the north of the Maule River, Chile. Gayana. 64(1): 110-116.