Pinaceae
Abies nebrodensis
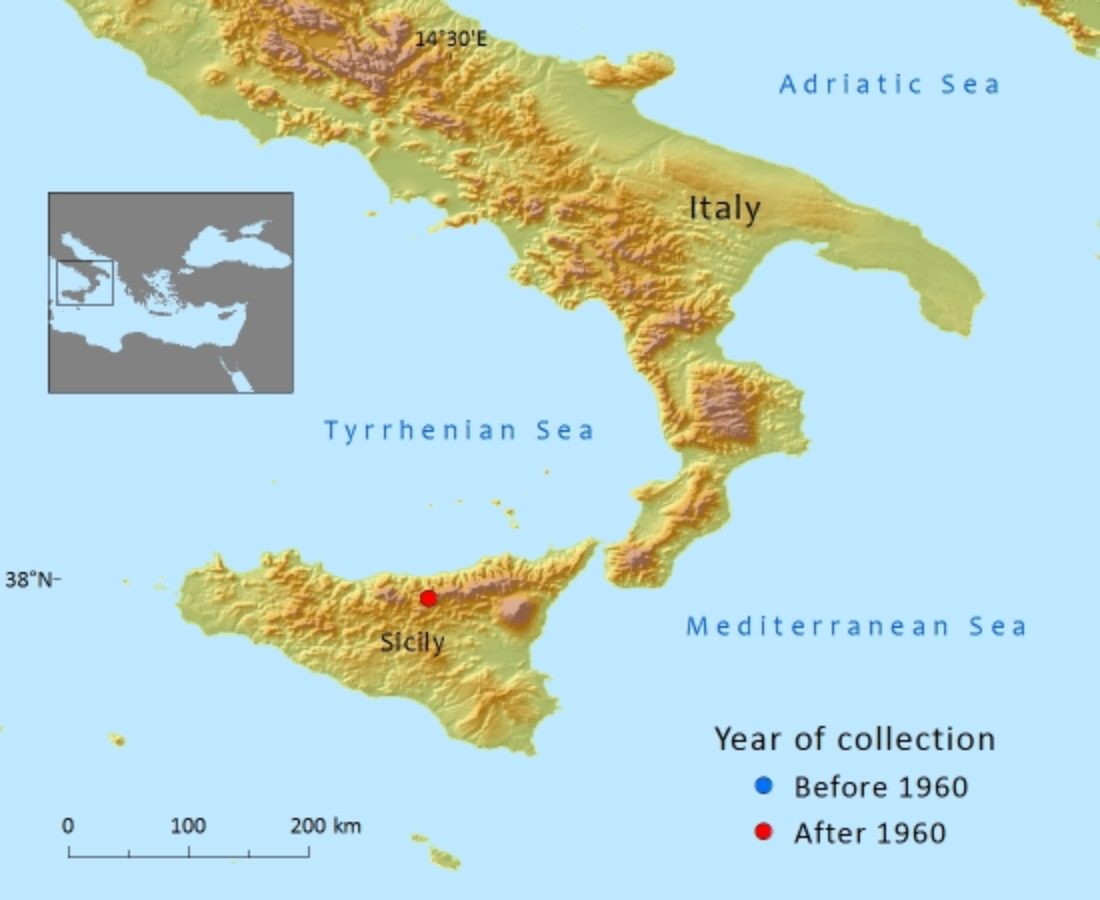
A narrow endemic native to the Madonie Mountains of Sicily where the entire population consists of only 30 individuals.
Description
Habit
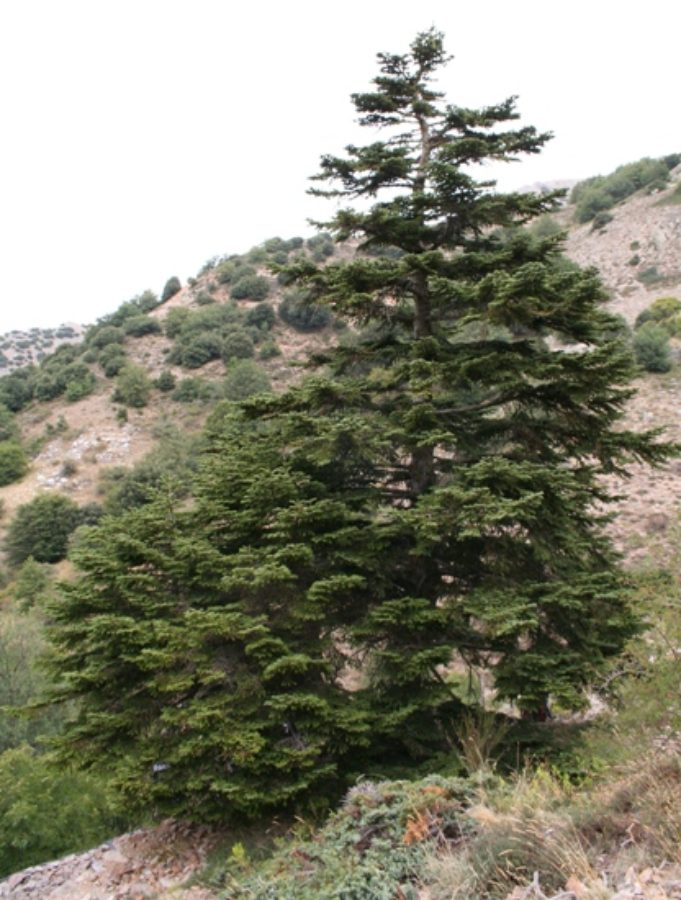
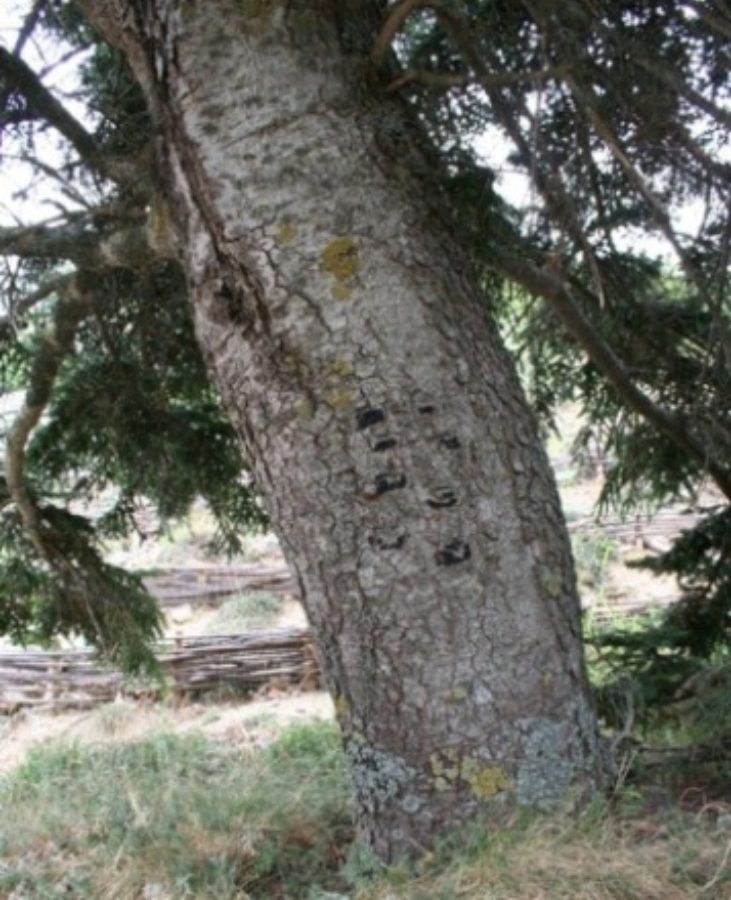
Forms a broad, conical tree between 15–18m tall. Branches spreading horizontally. Bark smooth in young trees but exfoliating in small plates with age, exposed bark brown, later grey.
Foliage
Leaves 1–2 x 2–3.5cm, spirally arranged, the upper leaves covering the shoot and directed forward, the lower parted with two greenish white stomatal bands beneath. Vegetative buds conical, slightly resinous.
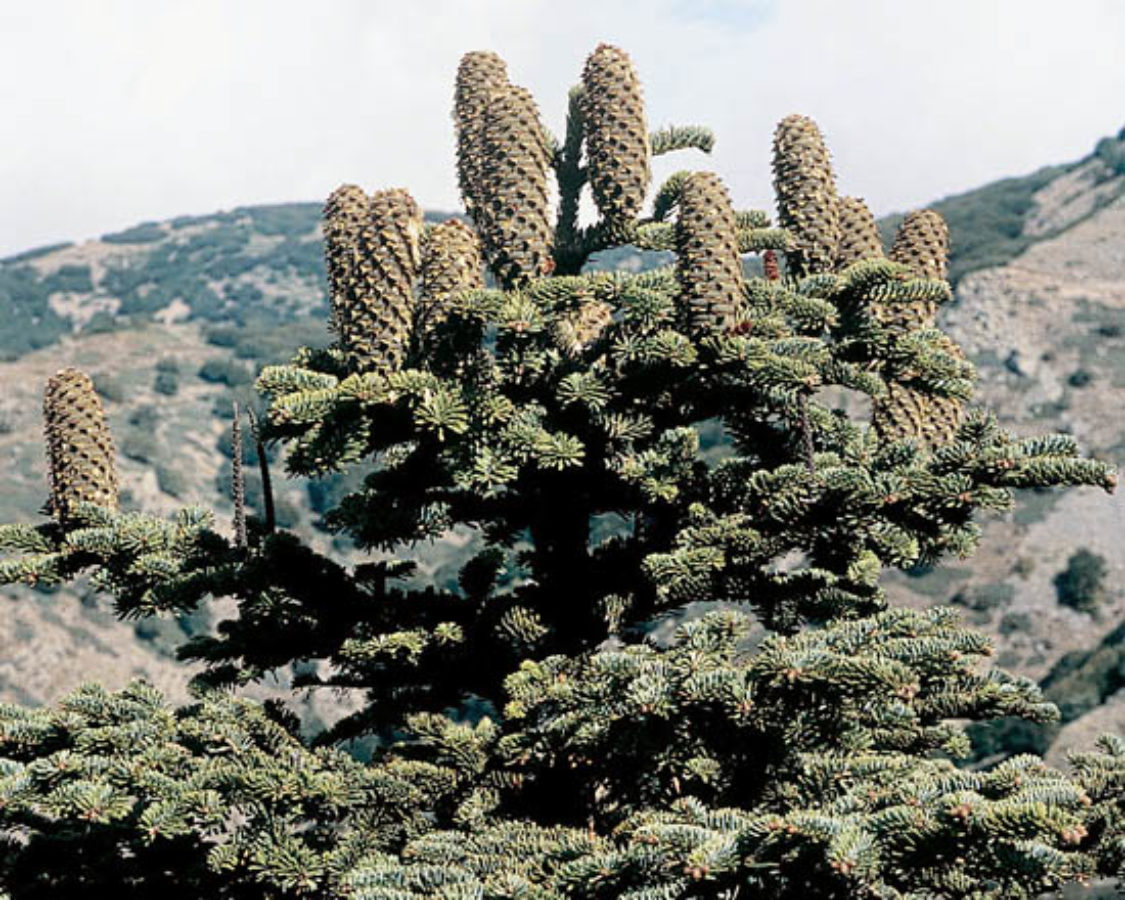
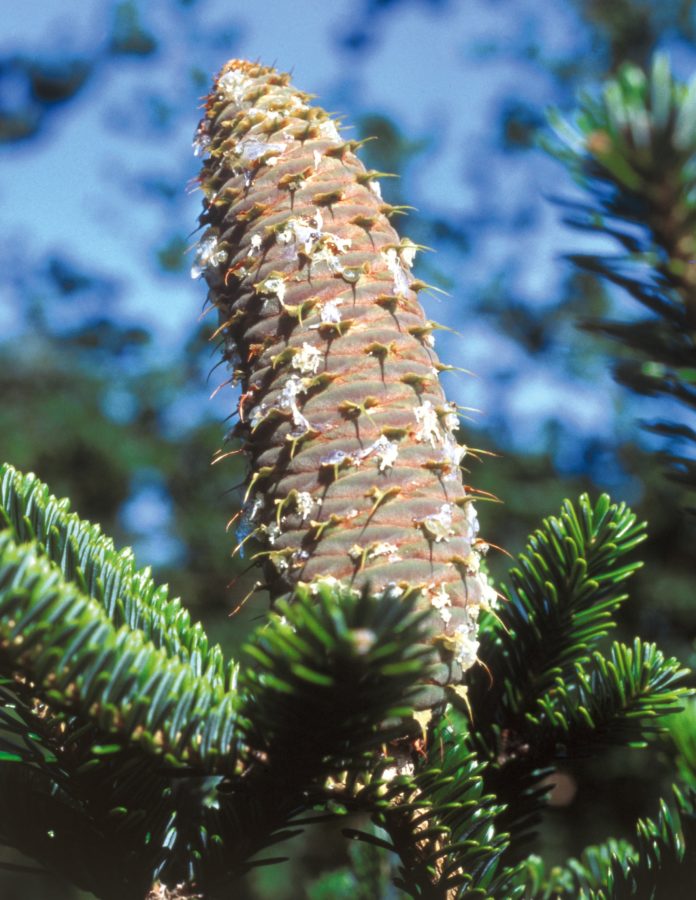
Cones
Female cones 10–18 cm, cylindrical, maturing from green or reddish-brown to brown; bracts exserted, reflexed, triangular and long pointed. Male cones lateral, crowded, 1.5-2 cm long, greenish yellow with purple microsporophylls.
Human Uses
This species is too rare to be exploited. Historically the timber was used for construction.
References and further reading
- Conte, L., Cotti,C., Schicchi, R., Raimondo,F. M. & G. Cristofolini. (2004). Detection of ephemeral genetic sub-structure in the narrow endemic Abies nebrodensis (Lojac.) Mattei (Pinaceae) using RAPD markers. Plant Biosystems. 138(3) 279-289.
- Ducci, F., Proietti, R. & J.–M. Favre. (1999). Allozyme assessment of genetic diversity within the relic Sicilian fir Abies nebrodensis (Lojac.). Mattei. Ann. For. Sci. 56: 345-355.
- Farjon, A. and Page, C.N. (compilers) (1999). Conifers. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN/SSC Conifer Specialist Group. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK.
- Knees, S.G. (2011). Phylogeny, Systematics and Conservation of Abies, especially those around the Mediterranean Basin. Reading. Unpublished PhD Thesis, University of Reading.
- Morandini,R. (1969). Abies nebrodensis (Lojac). Mattei. – Inventario 1968. Pubbl. Ist. Sper. Selvic. Arezzo
- Morandini, R., Ducci, F., & G. Menguzzat. (1994). Abies nebrodensis (Lojac.) Mattei. Inventario 1992. Ann. Ist. Sper: Selv. 22:5-5 1.
- Parducci, L., Szmidt, A.E, Ribeiro, M.N. & A. D.Drouzas. (2001). Taxonomic position and origin of the endemic Sicilian Fir Abies nebrodensis (Lojac.) Mattei based on allozyme analysis. Forest Genetics 8(2) 119-127.
- Raimondof, M., Venturella, G., & di Gangif. (1990). Variazioni fenotipiche in Abies nebrodensis (Lojac.) Mattei e comportamento vegetativo nella sua discendenza. Quaderni di Botanica Ambientale Applicatu. 1:183-2 10.
- Silva, J. P., Toland, J., Jones, W., Eldridge, J., Thorpe, E., Campbell, M. & E. O’Hara. (2008). LIFE and Europe’s endangered Abies nebrodensis.
- Sottano, P. (2004). Conservazione di Abies nebrodensis e ripristino torbiere di Geraci Siculo. Parco delle Madonie.
- Thomas, P. 2011. Abies nebrodensis. In: IUCN 2012. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . Downloaded on 07 March 2013.
- Vendramin, G.G., Michelozzi, M., Tognetti, R., F. Vicario. (1997). Abies nebrodensis (Lojac.) Mattei, a relevant example of a relic and highly endangered species. Bocconea 7: 383-388.
- Vicario, F., Vendramin, G. G, Rossi, P., Liò, P., & R. Giannini. (1995): Allozyme, chloroplast DNA and RAPD markers for determining genetic relationships between Abies alba and the relic population of Abies nebrodensis. Theoretical & Applied Genetics. 90: 101 2-101 8
- Virgilio, F., Schicchi, R. and La Mela Veca, D. (2000). Aggiornamento dell'inventario della popolazione relitta di Abies nebrodensis (Lojac.). Naturalista Siciliano 24 (1-2): 13–54