Pinaceae
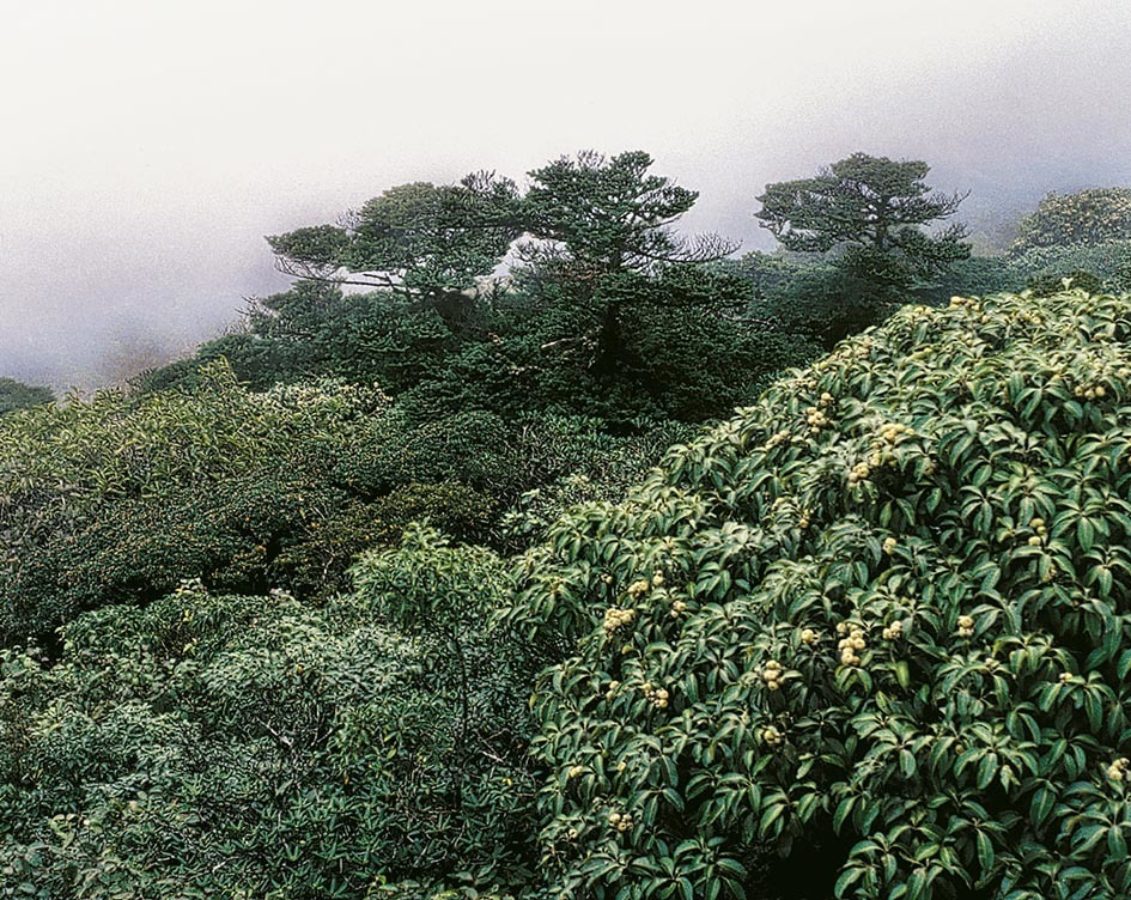
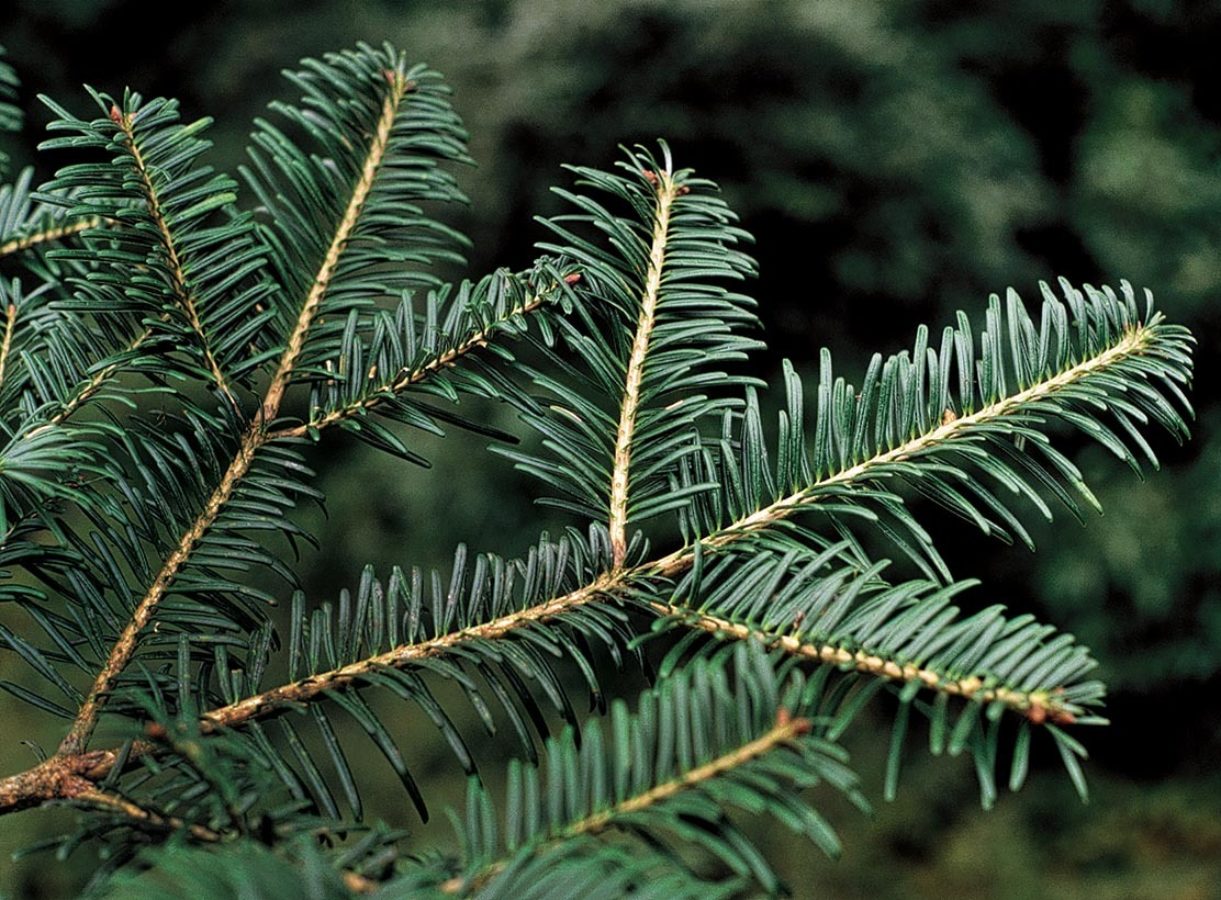
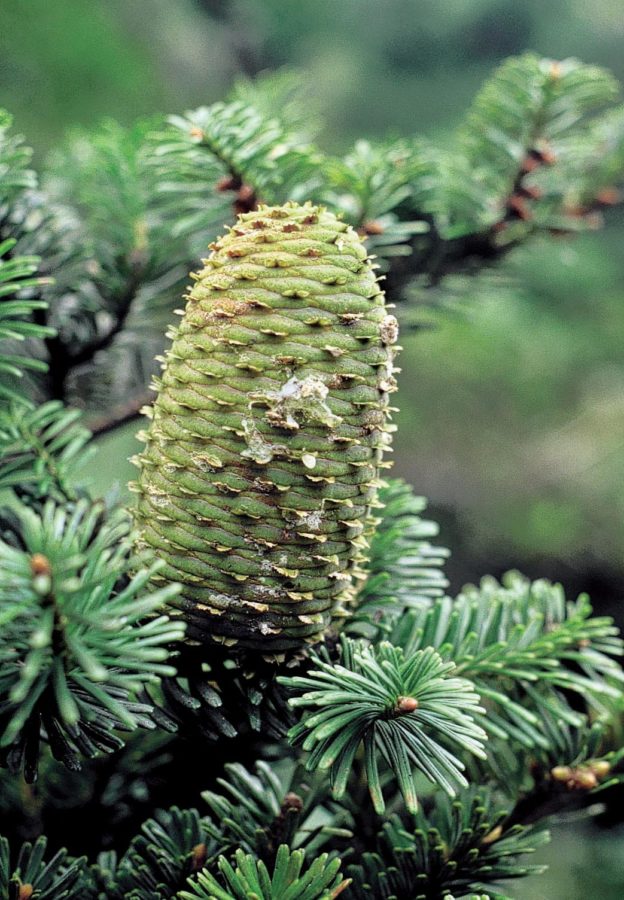
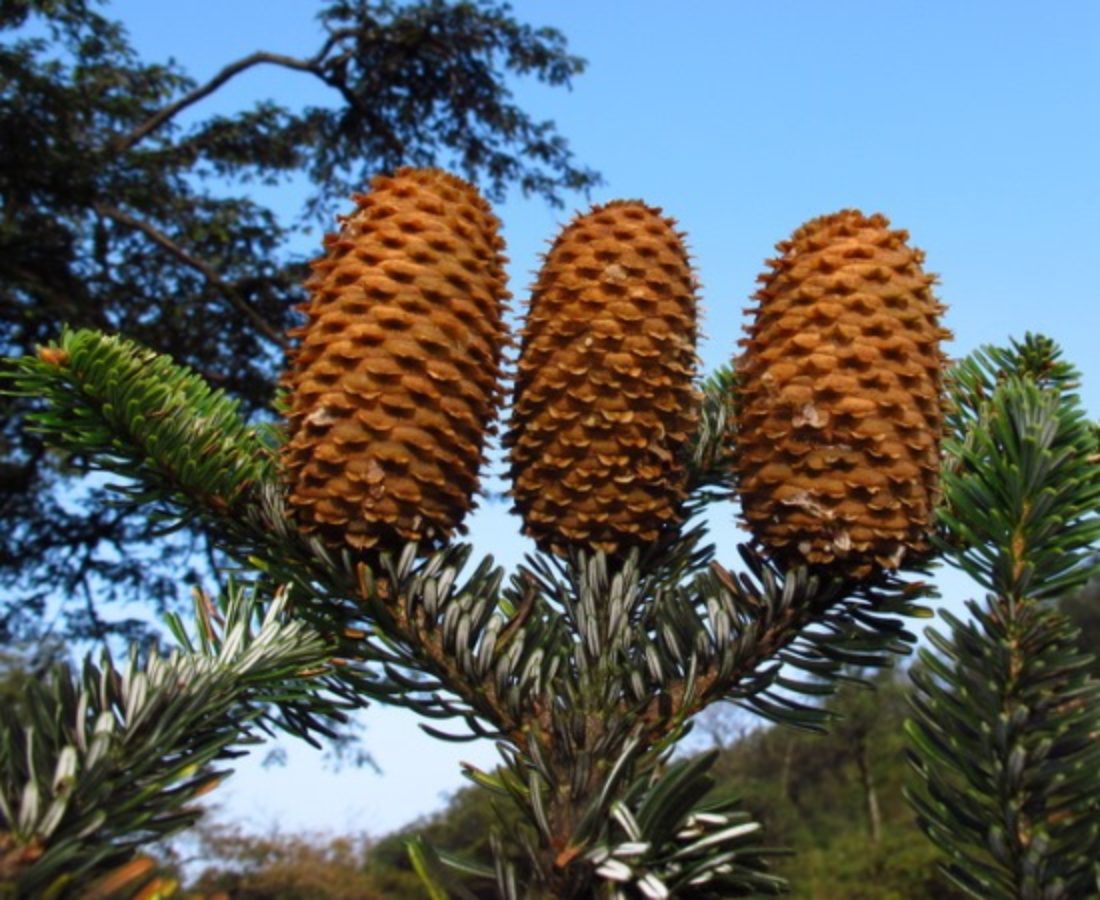
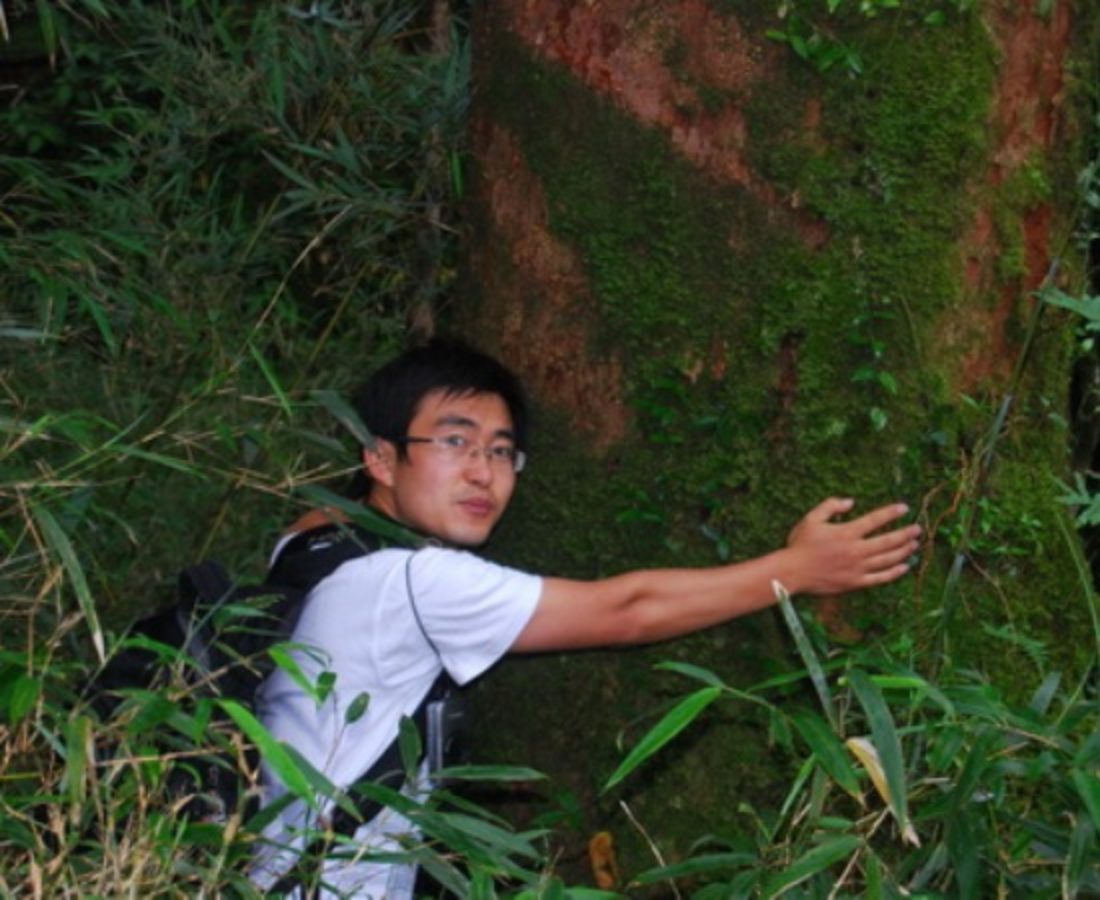
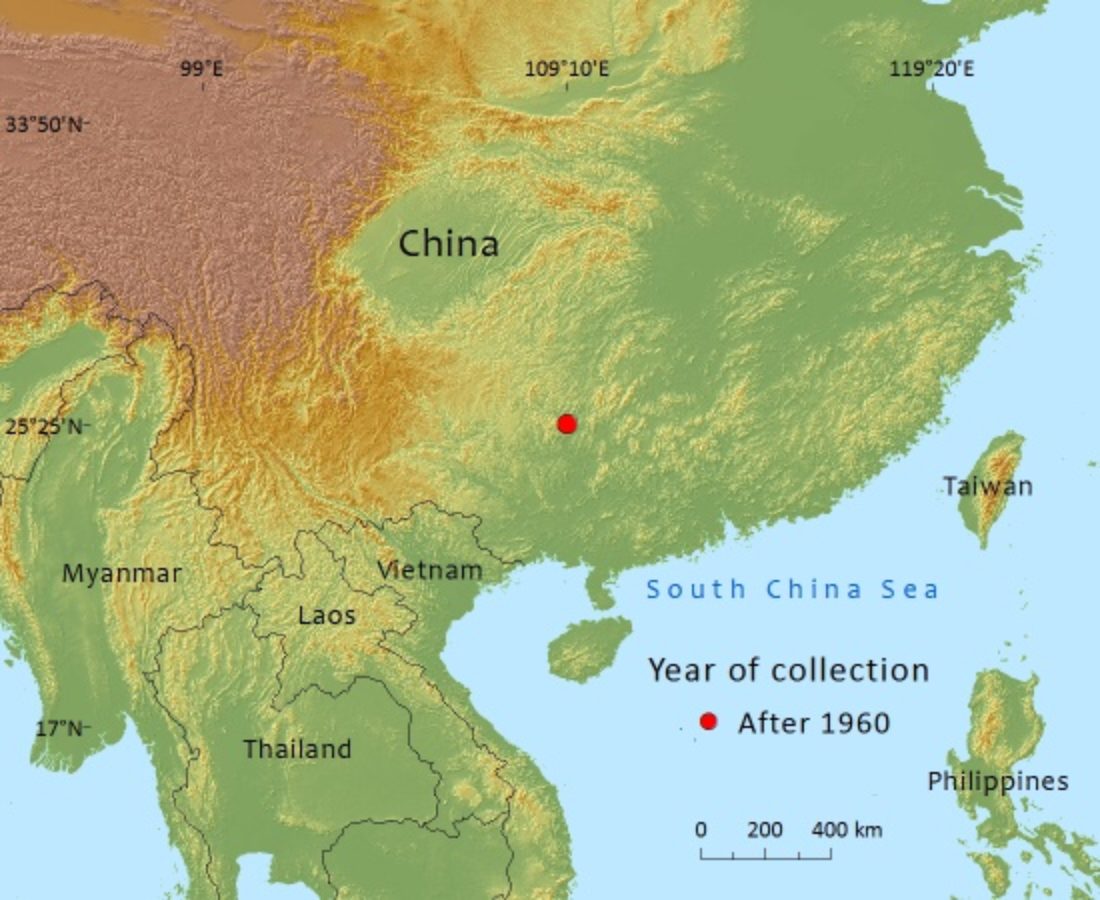
Abies yuanbaoshanensis
Endemic to south-east China where the population is only about 600 individuals
References and further reading
- Farjon, A. (2010). A Handbook of the World's Conifers. Koninklijke Brill, Leiden.
- Fu, L., Lu, Y. & Mo, S. (1980). The genus Abies discovered for the first time in Guangxi and Hunan. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica 18(2): 205.
- Farjon, A., Li, J.-y., Li, N., Li, Y., Carter, G., Katsuki, T., Liao, W., Luscombe, D, Qin, H.-n., Rao, L.-b., Rushforth, K., Yang, Y., Yu, S., Xiang, Q. & Zhang, D 2011. Abies yuanbaoshanensis. In: IUCN 2012. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . Downloaded on 05 April 2013.